Helen Caulfield
Royal National Throat, Nose and Ear Hospital. UK.
Title: The use of medical treatment to optimise respiratory function prior to adenotonsillectomy for sleep disordered breathing in the children under 3 years old
Biography
Biography: Helen Caulfield
Abstract
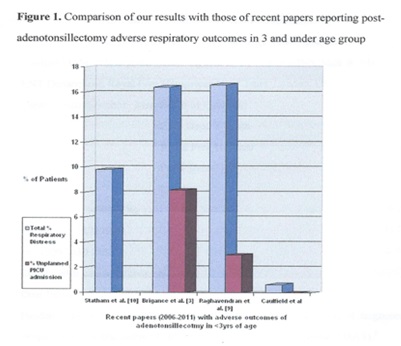
Paediatric sleep disordered breathing encompasses a spectrum ranging from simple snoring to obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome1. Adenotonsillectomy represents an effective treatment for sleep disordered breathing, but the literature reveals that children under 3 years are at greater risk of having more severe obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and higher rates of postoperative respiratory adverse events2,3. Suddenly relieving the hypercarbia present in some sleep disordered breathing patients by removing the upper airway obstruction can result in pulmonary oedema and acute respiratory failure.
The ENT_UK multidisciplinary working party consensus statement (2008) included children under 2 years (or under 15 kg) with sleep disordered breathing in the ‘at risk’ group. It was recommended that these children should be recovered in intensive care unit facilities5. It was noted that there is currently a lack of evidence for adverse respiratory outcomes in this country with no published case series. We present how we manage the under-3 year age group undergoing adentonsillectomy for sleep disordered breathing in a unit without a paediatric intensive care unit.